Variables and Data Types in Java
Variable is a name of memory location. There are three types of variables in java: local, instance and static.
There are two types of data types in java: primitive and non-primitive.
Variable
Variable is name of reserved area allocated in memory. In other words, it is a name of memory location. It is a combination of "vary + able" that means its value can be changed.

int data=50;//Here data is variable
Types of Variable
There are three types of variables in java:
- local variable
- instance variable
- static variable

1) Local Variable
A variable which is declared inside the method is called local variable.
2) Instance Variable
A variable which is declared inside the class but outside the method, is called instance variable . It is not declared as static.
3) Static variable
A variable that is declared as static is called static variable. It cannot be local.
We will have detailed learning of these variables in next chapters.
Example to understand the types of variables in java
class A{
int data=50;//instance variable
static int m=100;//static variable
void method(){
int n=90;//local variable
}
}//end of class
Data Types in Java
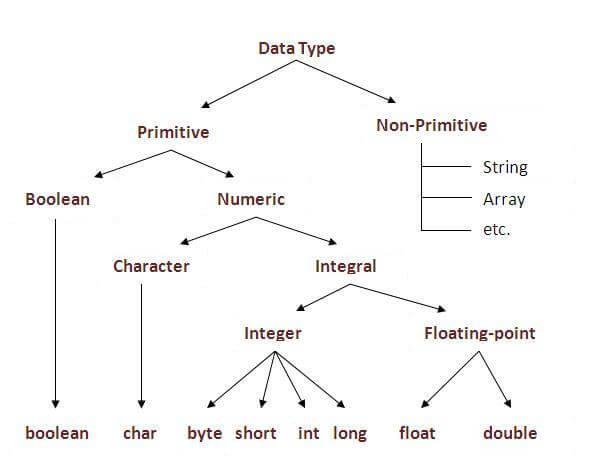
Data types represent the different values to be stored in the variable. In java, there are two types of data types:
- Primitive data types
- Non-primitive data types
| Data Type | Default Value | Default size |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | false | 1 bit |
| char | '\u0000' | 2 byte |
| byte | 0 | 1 byte |
| short | 0 | 2 byte |
| int | 0 | 4 byte |
| long | 0L | 8 byte |
| float | 0.0f | 4 byte |
| double | 0.0d | 8 byte |
Why char uses 2 byte in java and what is \u0000 ?
It is because java uses Unicode system than ASCII code system. The \u0000 is the lowest range of Unicode system. To get detail explanation about Unicode visit next page.
Java Variable Example: Add Two Numbers
class Simple{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a=10;
int b=10;
int c=a+b;
System.out.println(c);
}}
Output:
20
Java Variable Example: Widening
class Simple{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a=10;
float f=a;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(f);
}}
Output:
10 10.0
Java Variable Example: Narrowing (Typecasting)
class Simple{
public static void main(String[] args){
float f=10.5f;
//int a=f;//Compile time error
int a=(int)f;
System.out.println(f);
System.out.println(a);
}}
Output:
10.5 10
Java Variable Example: Overflow
class Simple{
public static void main(String[] args){
//Overflow
int a=130;
byte b=(byte)a;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}}
Output:
130 -126
Java Variable Example: Adding Lower Type
class Simple{
public static void main(String[] args){
byte a=10;
byte b=10;
//byte c=a+b;//Compile Time Error: because a+b=20 will be int
byte c=(byte)(a+b);
System.out.println(c);
}}
Output:
20
No comments:
Post a Comment