Creating hello java example
Let's create the hello java program:
class Simple{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello Java");
}
}
save this file as Simple.java
| To compile: | javac Simple.java |
| To execute: | java Simple |
Output:Hello Java
Understanding first java program
Let's see what is the meaning of class, public, static, void, main, String[], System.out.println().
- class keyword is used to declare a class in java.
- public keyword is an access modifier which represents visibility, it means it is visible to all.
- static is a keyword, if we declare any method as static, it is known as static method. The core advantage of static method is that there is no need to create object to invoke the static method. The main method is executed by the JVM, so it doesn't require to create object to invoke the main method. So it saves memory.
- void is the return type of the method, it means it doesn't return any value.
- main represents startup of the program.
- String[] args is used for command line argument. We will learn it later.
- System.out.println() is used print statement. We will learn about the internal working of System.out.println statement later.
To write the simple program, open notepad by start menu -> All Programs -> Accessories -> notepad and write simple program as displayed below:
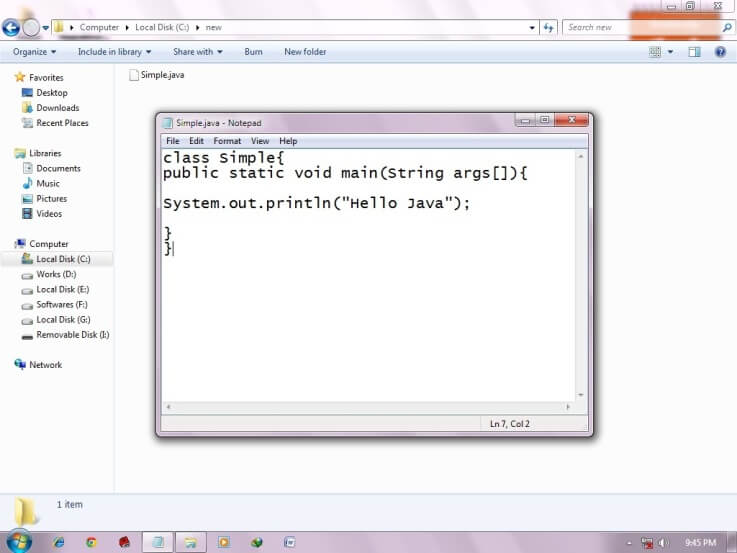
| As displayed in the above diagram, write the simple program of java in notepad and saved it as Simple.java. To compile and run this program, you need to open command prompt by start menu -> All Programs -> Accessories -> command prompt. |
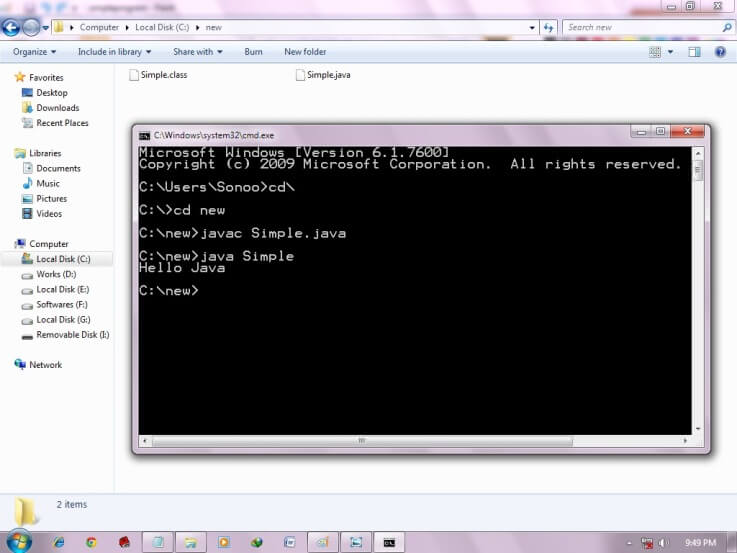
| To compile and run the above program, go to your current directory first; my current directory is c:\new . Write here: |
| To compile: | javac Simple.java |
| To execute: | java Simple |
How many ways can we write a java program
There are many ways to write a java program. The modifications that can be done in a java program are given below:
1) By changing sequence of the modifiers, method prototype is not changed.
Let's see the simple code of main method.
static public void main(String args[])
2) subscript notation in java array can be used after type, before variable or after variable.
Let's see the different codes to write the main method.
public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String []args)
public static void main(String args[])
3) You can provide var-args support to main method by passing 3 ellipses (dots)
Let's see the simple code of using var-args in main method. We will learn about var-args later in Java New Features chapter.
4) Having semicolon at the end of class in java is optional.
Let's see the simple code.
class A{
static public void main(String... args){
System.out.println("hello java4");
}
};
Valid java main method signature
public static void main(String[] args)
public static void main(String []args)
public static void main(String args[])
public static void main(String... args)
static public void main(String[] args)
public static final void main(String[] args)
final public static void main(String[] args)
final strictfp public static void main(String[] args)
Invalid java main method signature
public void main(String[] args)
static void main(String[] args)
public void static main(String[] args)
abstract public static void main(String[] args)
No comments:
Post a Comment