Java Switch Statement
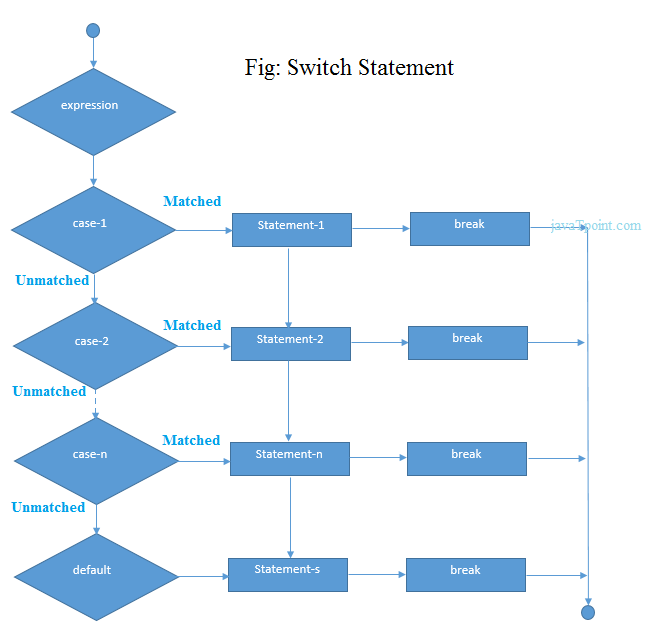
The Java switch statement executes one statement from multiple conditions. It is like if-else-if ladder statement.
Syntax:
switch(expression){
case value1:
//code to be executed;
break; //optional
case value2:
//code to be executed;
break; //optional
......
default:
code to be executed if all cases are not matched;
}
Example:
public class SwitchExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number=20;
switch(number){
case 10: System.out.println("10");break;
case 20: System.out.println("20");break;
case 30: System.out.println("30");break;
default:System.out.println("Not in 10, 20 or 30");
}
}
}
Output:
20
Java Switch Statement is fall-through
The java switch statement is fall-through. It means it executes all statement after first match if break statement is not used with switch cases.
Example:
public class SwitchExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number=20;
switch(number){
case 10: System.out.println("10");
case 20: System.out.println("20");
case 30: System.out.println("30");
default:System.out.println("Not in 10, 20 or 30");
}
}
}
Output:
20 30 Not in 10, 20 or 30
No comments:
Post a Comment