Java static keyword
The static keyword in java is used for memory management mainly. We can apply java static keyword with variables, methods, blocks and nested class. The static keyword belongs to the class than instance of the class.
The static can be:
- variable (also known as class variable)
- method (also known as class method)
- block
- nested class
1) Java static variable
If you declare any variable as static, it is known static variable.
- The static variable can be used to refer the common property of all objects (that is not unique for each object) e.g. company name of employees,college name of students etc.
- The static variable gets memory only once in class area at the time of class loading.
Advantage of static variable
It makes your program memory efficient (i.e it saves memory).
Understanding problem without static variable
class Student{
int rollno;
String name;
String college="ITS";
}
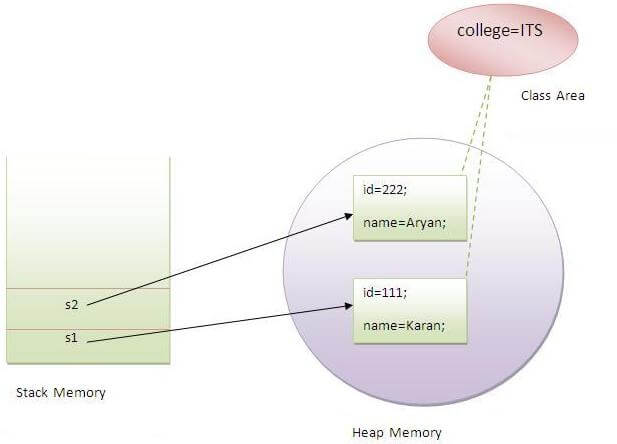
Suppose there are 500 students in my college, now all instance data members will get memory each time when object is created.All student have its unique rollno and name so instance data member is good.Here, college refers to the common property of all objects.If we make it static,this field will get memory only once.
Note: Java static property is shared to all objects.
Note: Java static property is shared to all objects.
Example of static variable
//Program of static variable
class Student8{
int rollno;
String name;
static String college ="ITS";
Student8(int r,String n){
rollno = r;
name = n;
}
void display (){System.out.println(rollno+" "+name+" "+college);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student8 s1 = new Student8(111,"Karan");
Student8 s2 = new Student8(222,"Aryan");
s1.display();
s2.display();
}
}
Output:111 Karan ITS
222 Aryan ITS
Program of counter without static variable
In this example, we have created an instance variable named count which is incremented in the constructor. Since instance variable gets the memory at the time of object creation, each object will have the copy of the instance variable, if it is incremented, it won't reflect to other objects. So each objects will have the value 1 in the count variable.
class Counter{
int count=0;//will get memory when instance is created
Counter(){
count++;
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Counter c1=new Counter();
Counter c2=new Counter();
Counter c3=new Counter();
}
}
Output:1
1
1
Program of counter by static variable
| As we have mentioned above, static variable will get the memory only once, if any object changes the value of the static variable, it will retain its value. |
class Counter2{
static int count=0;//will get memory only once and retain its value
Counter2(){
count++;
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Counter2 c1=new Counter2();
Counter2 c2=new Counter2();
Counter2 c3=new Counter2();
}
}
Output:1
2
3
2) Java static method
If you apply static keyword with any method, it is known as static method.
- A static method belongs to the class rather than object of a class.
- A static method can be invoked without the need for creating an instance of a class.
- static method can access static data member and can change the value of it.
Example of static method
//Program of changing the common property of all objects(static field).
class Student9{
int rollno;
String name;
static String college = "ITS";
static void change(){
college = "BBDIT";
}
Student9(int r, String n){
rollno = r;
name = n;
}
void display (){System.out.println(rollno+" "+name+" "+college);}
public static void main(String args[]){
Student9.change();
Student9 s1 = new Student9 (111,"Karan");
Student9 s2 = new Student9 (222,"Aryan");
Student9 s3 = new Student9 (333,"Sonoo");
s1.display();
s2.display();
s3.display();
}
}
Output:111 Karan BBDIT
222 Aryan BBDIT
333 Sonoo BBDIT
Another example of static method that performs normal calculation
//Program to get cube of a given number by static method
class Calculate{
static int cube(int x){
return x*x*x;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int result=Calculate.cube(5);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Output:125
Restrictions for static method
| There are two main restrictions for the static method. They are: |
class A{
int a=40;//non static
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(a);
}
}
Output:Compile Time Error
Q) why java main method is static?
3) Java static block
Example of static block
class A2{
static{System.out.println("static block is invoked");}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello main");
}
}
Output:static block is invoked
Hello main
|
No comments:
Post a Comment